Big Data Technologies

By Hiren Rupchandani and Abhinav Jangir
- Data is the new fuel that is driving most of the industries and businesses in this decade.
- Every industry generates data in one form or another — let it be a tabular, image, textual, acoustic signal, sensor data through IoT devices, and whatnot.
- These data originate from various industries like retail, finance, healthcare, manufacturing, social media, banking, and many more.
- With the advent of the Internet and better processing capabilities of computers, a lot of data is generated throughout the globe and it is either being exchanged, stored, processed, or analyzed by many organizations.
What is Big data?
- Data generation is growing exponentially with time and thus its complexity increases as well.
- Traditional data processing methods are not efficient enough to process or store these copious amounts of data.
- Such complex and highly volumetric data is known as Big Data.
In very simple words, Big Data is nothing but a huge amount of data.
How much Data are we generating?
- People, businesses, and devices are pumping out incredible amounts of information to the web each day.
- By the end of 2020, the amount of data stored was estimated to be 44 zettabytes around the globe.
- By 2025, the amount of data generated each day is expected to reach 463 exabytes globally.
- Google, Facebook (now Meta), Microsoft, and Amazon store at least 1,200 petabytes of information.
The 6 Vs of Big Data
To properly describe the characteristics of big data, we must understand the 6 Vs of big data. They are as follows:

1. Volume
- Volume indicates the size of the data that is being generated and stored in systems.
- Today’s systems are not powerful and fast enough to process large volumes of data in one go.
2. Variety
- Variety talks about the wide variety of data that is being stored and still needs to be processed and analyzed.
- Different types of data (structured, unstructured, and semi-structured) are readily being generated from social networks, banks, businesses, and mobile devices, among others.
3. Velocity
- It indicates the rate at which data is being generated.
- Even with powerful systems, the sources from which data is being generated are unprecedented and cannot be kept in check at the same time.
4. Value
- This V talks about how valuable insights are you able to generate and use from the copious amount of data that you have stored.
- Just keeping the data in a data lake won’t make it useful, organizations need to hire experts who can process the data and gain valuable and actionable insights from it.
5. Veracity
- Veracity shows the quality and origin of data, allows it to be considered questionable, conflicting, or impure, and provides information about matters you are not sure how to deal with.
6. Variability
- Finally, variability: to what extent is the structure of your data changing?
- And how often does the meaning or shape of your data change?
Tasks that can be performed using Big Data
Comparative analysis
- Using big data, a company can analyze the behavior patterns of its customers in real-time and compare its product offerings with those of its competitors.
Social media listening
- Social media collects a lot of user data that can be used by companies (like Meta) to target not only products but a lot of other resources through tailored advertisements.
Marketing analytics
- Marketing data be used to generate insights which in turn can help improve future marketing campaigns and promotional offers for products, services, and business initiatives.
Sentiment analysis
- Customer satisfaction and support play a prominent role in a business’s success.
- The Internet has made it possible to collect user feedback that can be in turn used to determine whether a customer was satisfied with the product or service or not.
Widely Used Big Data Technologies
Big Data requires entirely new technologies and algorithms to process and store it.
Apache Hadoop
Apache Hadoop is one of the leading open source big data analytics tools. It is a framework used to store data and run big data applications on clusters consisting of consumer systems.

Hadoop uses a primary system named Hadoop Distributed File Systems or HDFS as well as a supporting system called MapReduce. These enable the Hadoop ecosystem to quickly and efficiently perform storage and processing tasks across clusters (consisting of consumer systems) with minimal cost. It means that you can perform big data analytics relatively cheaper. Some of the features that made Hadoop popular are as follows:
- Easy to Use and Open Source
- Highly Scalable Cluster
- Fault Tolerance is Available
- High Availability is Provided
- Cost-Effective
- High Flexibility Provided
- Hadoop uses Data Locality
Apache Kafka
Apache Kafka is a distributed data store that is optimized for ingestion and processing of streaming data in real-time. Streaming data is the data that is being produced regularly by a plethora of sources and needs to be stored or processed on a constant basis.

Kafka combines messaging, storage, and stream processing to allow storage and analysis of both historical and real-time data. It handles streaming data by providing three main functions to its users:
- Publish and subscribe to streams of record
- Effectively store streams of records in the order in which records were generated
- Process streams of records in real-time
Apache Cassandra
Cassandra is an open-source distributed database management system with a wide column store, NoSQL database to handle a large amount of data across many commodity servers which provides high availability with no single point of failure.

It is developed by Apache Software Foundation and written in Java. Some of the features of Cassandra are as follows:
- It is scalable, fault-tolerant, and consistent.
- It is a column-oriented database.
- Its distributed design is based on Amazon’s Dynamo and its data model on Google’s Big Table.
- It differs sharply from relational database management systems.
Apache Hive
Apache Hive is a data warehouse and an ETL tool that provides an SQL-like interface between the user and the HDFS. It is built on top of Hadoop and is frequently used for data warehousing tasks like data encapsulation, Ad-hoc Queries, and analysis of huge datasets.

It allows for scalability, extensibility, performance, fault-tolerance, and loose-coupling with its input formats. Some of the additional features are as follows:
- Metadata storage in an RDBMS that reduces the time to function
- Allows for user-defined functions to manipulate dates, strings, and other data-mining tools
- It stores schemas in a database and processes the data into the HDFS
- It is built for Online Analytical Processing OLAP and not Online Transactional Processing (OLTP)
- It delivers a type of querying language known as Hive Query Language (HiveQL or HVL)
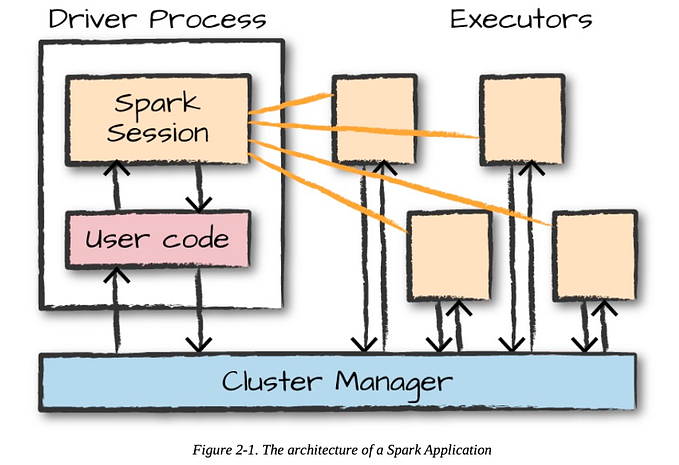
Apache Spark
Apache Spark is one of the best and most powerful open source big data analytics tools. Its framework allows the user to process a large number of data sets. It is pretty easy to distribute data processing tasks across multiple computers with its conjunction or with other distributed computing tools.
It provides features for streaming SQL, machine learning, and graph processing. Spark has proven very popular and is used by many large companies for huge, multi-petabyte data storage and analysis.

In a benchmark test involving sorting 100 terabytes of data, Spark took 23 minutes to finish the test and broke the world record which was previously held by Hadoop for 71 minutes.
Apart from that, it also has around 80 high-level operators to build parallel apps more quickly and is also highly flexible and versatile since it works with different data stores like HDFS and Cassandra.
Use Cases of Big Data Solutions in industries
Meta
- Facebook (or Meta) is one of the popular Social Networking Websites. Worldwide, around 1 billion users are using Facebook, Instagram, and Whatsapp.
- It collects more than 500TB (Tera Bytes) of data per day from its userbase.
- User Likes, Posts, Relations Information, Audio, Videos, Pictures, etc contribute a lot to this data generation.

- Google has its own Big Data Cloud Platform to manage their applications data like Gmail, GDrive, Google Search Engine, YouTube, etc.
Aadhar India

- UIDAI (Unique Identification Authority Of India) manages all Aadhar Card information which amounts to storing data of at least a billion people.
- Without adequate big data technologies, it wouldn’t have been possible to store this information.
New York Stock Exchange

- The New York Stock Exchange generates about 5 TB (Tera Bytes) of data per day.
Conclusion
- And here it is —a very descriptive information of one of the most important technologies available to us today — Big Data.
- In the coming articles, we will be covering several big data analytics tools, starting with PySpark and Apache Hadoop.